Batch REST API#
Coiled Batch jobs are a lightweight API that make it easy to run your code on any cloud hardware and scale out parallel workflows. The Batch REST API allows you to submit jobs from anywhere you can make a web request. This is useful for:
Submitting large workloads from event-driven applications (FastAPI app, AWS EventBridge, etc.).
Working with fire-and-forget-style workflows or asynchronous architectures.
Keeping minimal dependencies. The REST API doesn’t need Python or the
coiledlibrary to be installed.Maintaining clear API request boundaries.
Quickstart#
To submit a job to Coiled via the REST API, first set the COILED_API_TOKEN environment variable to a Coiled API token used to authenticate this HTTP request. You can either create an API token at cloud.coiled.io/profile, or log in from the command line to create a token (if you haven’t already) and then use that token:
coiled login # If you haven't already
COILED_API_TOKEN=$(dask config get coiled.token)
Then submit a POST request, authenticated using the API token, along with the script to run. Here’s an example that runs the Bash echo command:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data '{"script":"echo hello"}'
This particular example uses curl for submitting the HTTP request from the terminal, but anything that submits HTTP requests can be used (for example, requests, wget, httpx, etc.).
Once Coiled receives your HTTP request, it will spin up appropriate machines defined by the request, download your software onto them, run your script, and then shut down the machines once your script is finished.
Configuration#
Use HTTP post data to easily customize the hardware and software resources for your job.
Manage Software#
By default, jobs will run inside a Docker container with the daskdev/dask image. You can also easily specify your own Docker container using "container" in the HTTP request data:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script": "echo hello",
"container": "my/image"
}'
You can use public images, private images in ECR (if you’re running on AWS), or can be configured to use any authenticated Docker registry.
Additionally, you can also use a manual software environment from an explicit environment.yml or requirements.txt. For example, if you have a requirements.txt file, you can use coiled env create to create a manual software environment that can then be used in the Batch REST API call:
# You just need to create the software environment once...
coiled env create --pip requirements.txt --name example-env
# Then you can use it in HTTP requests
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script": "echo hello",
"software": "example-env"
}'
You can specify the script your job should run in a few different ways.
Include the contents of your commands directly in "script". Here’s an example that runs the Bash echo command:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data '{"script":"echo hello"}'
Include Python code directly in "script" – be sure to set "python": true in the HTTP data too:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script":"print(\"hello from Python\")",
"python": true
}'
For longer scripts, you probably don’t want to include the full script in the HTTP request, so you can run code downloaded from a public URL:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script_uri":"https://gist.githubusercontent.com/ntabris/6d8bcad884c70252ab614cad982d46ab/raw/4763a1c91cf800abd1500fa01b8b32281cfb0d30/hello.py",
"python": true
}'
When using Coiled on AWS, you can run a script stored in an S3 bucket:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script_uri":"s3://my-bucket/example/hello.py",
"python": true
}'
For S3 bucket access, grant the relevant permissions to the IAM Role that’s used by the AWS Instance Profile that Coiled attaches to your AWS EC2 instance.
Manage Hardware#
Select any VM type available on your cloud (see VM Size and Type) with HTTP post data.
For example, to run the same echo command on an m6i.8xlarge instance in region us-west-2 on AWS, include vm_type and region parameters in the HTTP post data like this:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script":"echo hello",
"vm_type": "m6i.8xlarge",
"region": "us-west-2"
}'
Observability#
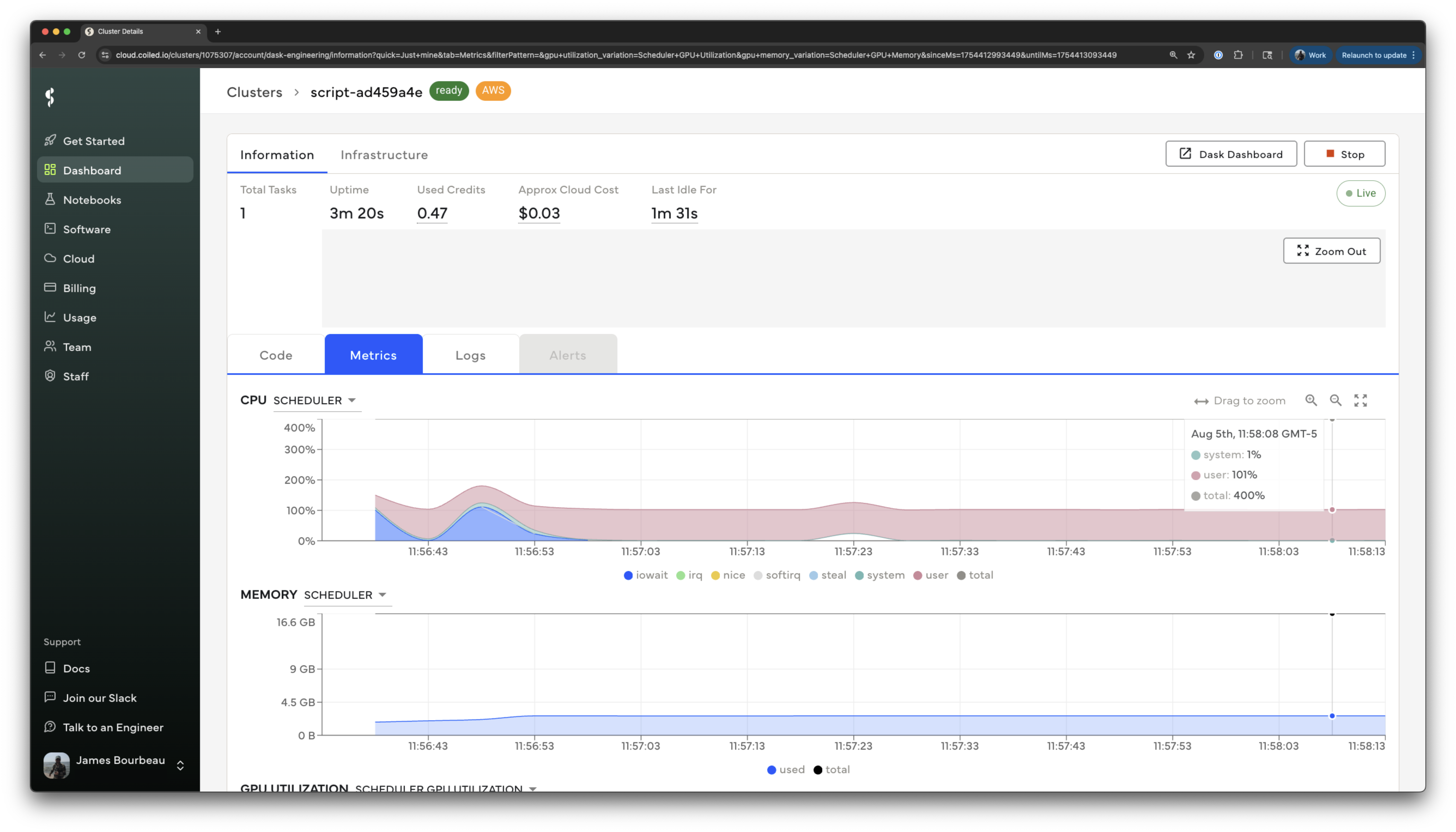
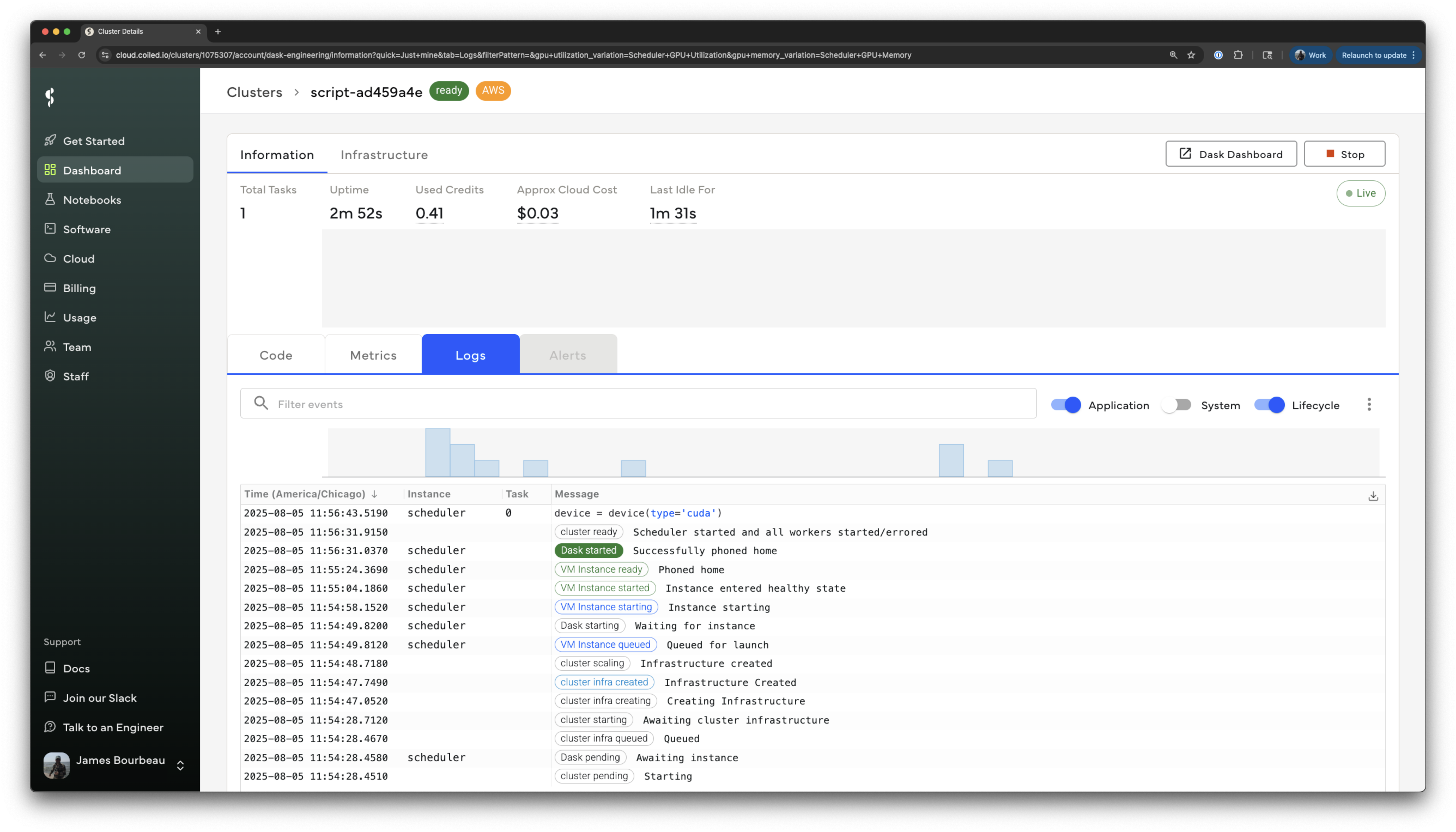
Batch jobs run remotely on cloud VMs in the background. You can easily view job hardware metrics, logs, cloud costs, and more at cloud.coiled.io.
Dask Integration#
Typically when using a Coiled Dask cluster, you’ll starts a cluster from your local machine (usually a laptop) then submits computations from your local machine to run on the cluster. This works well for many use cases, but when running large Dask computations triggered from a production system like, for example, AWS EventBridge, submitting Dask jobs asynchronously is often a better fit.
The Batch REST API makes it straightforward to submit Dask jobs via an HTTP request. For example, you can easily add worker VMs to a Dask cluster when submitting a job:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script_uri":"...",
"python": true,
"software": "...",
"workers": 20
}'
or with more configuration:
curl "https://cloud.coiled.io/api/v2/jobs/single-job-script/" \
--header "Authorization: ApiToken $COILED_API_TOKEN" \
--request POST \
--data $'{
"script_uri":"...",
"python": true,
"software": "...",
"workers": 20,
"vm_type": "m7g.large",
"worker_disk_size": 100,
"cluster_options": {"spot": true, "spot_on_demand_fallback": true}
}'
Then have the script you submit itself use this full Coiled Dask cluster.
In the script you’re submitting to Coiled, use coiled.get_dask_client_from_batch_node() to get a Dask client that’s connected to the cluster provisioned via the REST API.
import coiled
# Connect to the Coiled Dask cluster provisioned from the REST API
client = coiled.get_dask_client_from_batch_node()
# Existing Dask code will automatically run on the cluster
import dask
# generate random timeseries of data
df = dask.datasets.timeseries(
"1980", "2005", partition_freq="2w"
).persist()
# perform a groupby with an aggregation
result = df.groupby("name").aggregate({"x": "sum", "y": "max"}).compute()
print(result)
Note that to use coiled.get_dask_client_from_batch_node() you’ll need a Docker image or software environment that includes the coiled package.